需要用到深度学习编译框架来适配设计的学习加速器后端,学习了TVM、XLA、nGraph、DLVM等相关的工具,在这里对其作简单的介绍。
1. Introduction
目前类似的编译框架以TVM较为流行,主要还包括Google推出的基于TensorFlow的XLA, Intel推出的nGraph、以及伊利诺伊大学的DLVM项目等。
2. TVM
TVM: An Automated End-to-End Optimizing Compiler for Deep Learning. TVM 是由陈天奇团队发布的,应用于CPU、GPU以及专用加速器的深度学习编译框架(Compiler Stack),是一种将深度学习工作负载部署到硬件的端到端IR(中间表示)堆栈。换一种说法,可以表述为一种把深度学习模型分发到各种硬件设备上的、端到端的解决方案。旨在缩小深度学习框架和后端的硬件设备之间的鸿沟。可以通过框架将深度学习部署到CPU、GPU、专用加速器等,乃至可以部署到比如手机、树莓派等设备。
TVM的主要作用与意义是:
- 为不同硬件后端的深度学习工作负载提供性能可移植性的框架。
- 提供新颖的调度原语,它们利用了跨线程内存重用,新颖的硬件内在函数和延迟隐藏。
- 提出并实现了基于机器学习的优化系统,以自动探索和搜索优化的张量运算符。
- 构建了一个端到端的编译和优化堆栈,允许将高级框架(包括TensorFlow,MXNet,PyTorch,Keras,CNTK)中指定的深度学习工作负载部署到各种硬件后端(包括CPU,服务器GPU,移动GPU和基于FPGA的加速器)。
2.1 TVM的结构框架
TVM的系统结构图如下:
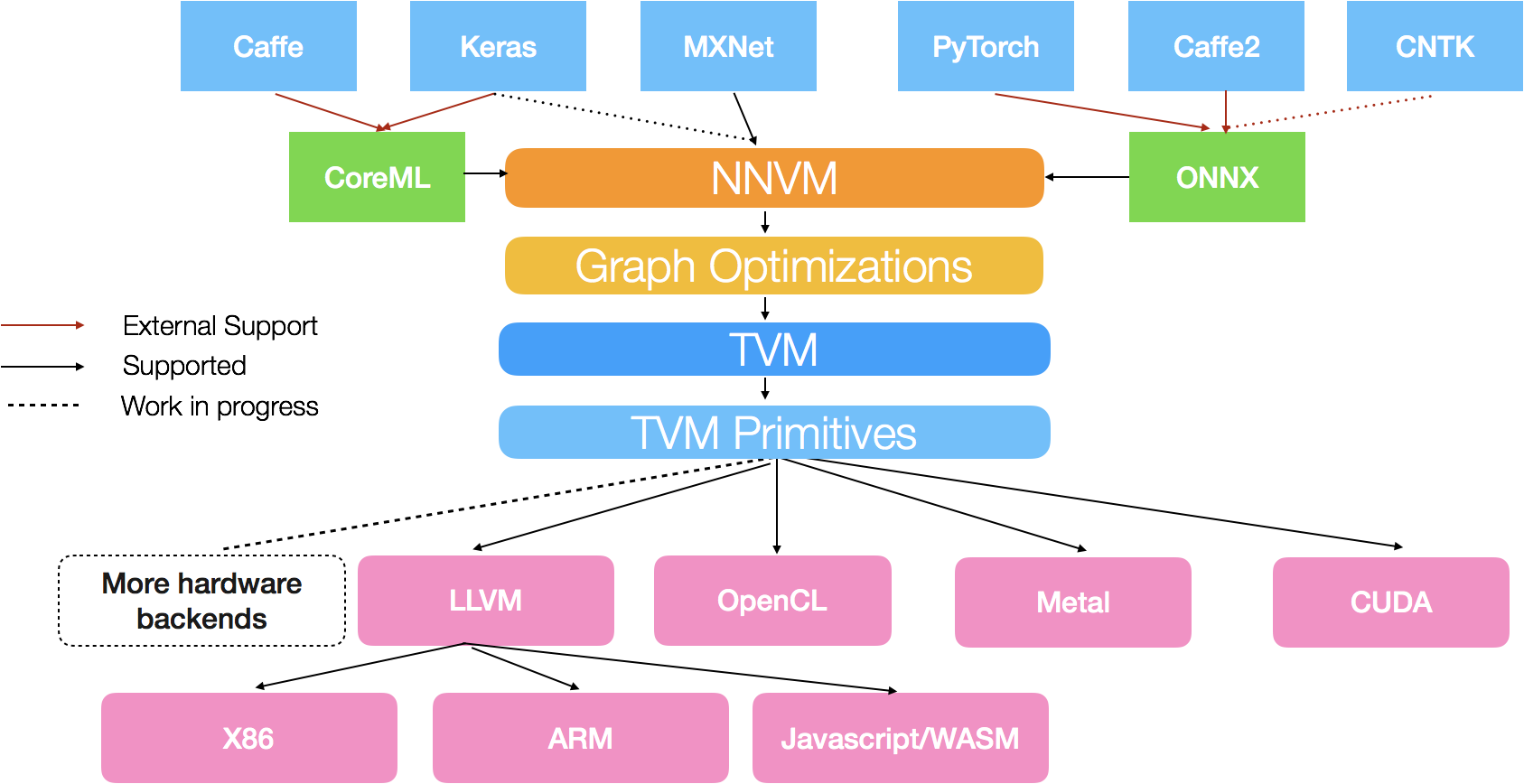
TVM的系统流程图如下:
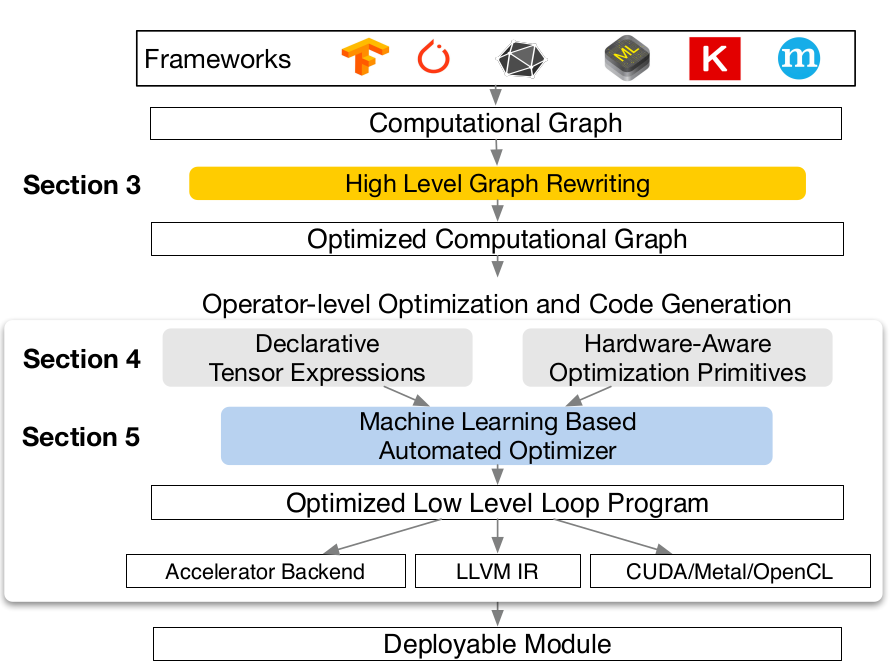
从图中,TVM的流程如下:
- 计算图IR的转换;
- Graph 优化;
- Tensor expression;
- schedule;
- Auto-Tuning;
- 生成二进制程序;
- 生成module.
2.2 前端与后端
TVM前端支持多种框架,后端支持多种硬件。如前面的结构图所示,前端框架的对接需要进行相应的IR转化。
使用Keras框架的例子如下:
import tvm as t
# Use keras framework as example, import model
graph, params = t.frontend.from_keras(keras_model)
target = t.target.cuda()
graph, lib, params = t.compiler.build(graph, target, params)
后端同样支持多种的硬件。对于N GPU, 使用了Cuda,如下:
import tvm.runtime as t
# Use Cuda for N GPU
module = runtime.create(graph, lib, t.cuda(0))
module.set_input(**params)
module.run(data=data_array)
output = tvm.nd.empty(out_shape, ctx=t.cuda(0))
module.get_output(0, output)
2.3 图优化 Graph
图优化主要包含:
- operator fusion: 把多个独立的operator融合成一个;
- constant-folding: 把一些可以静态计算出来的常量提前计算出来;
- static memory planning pass: 预先把需要的存储空间申请下来,避免动态分配;
- data layout transformations: 有些特殊的计算设备可能会对不同的data layout (i.e. NCHW, NHWC, HWCN)有不同的性能,TVM可以根据实际需求在graph层面就做好这些转换。
2.4 Tensor
- domain specific tensor expression
- decouple algorithm from schedule(解耦计算方法和具体调度)
- 可以用于定义很多常见的数学操作,但并没有指定具体的底层代码该如何实现(比如矩阵乘法计算时先遍历y方向还是先遍历x方向等)
m, n, h = t.var('m'), t.var('n'), t.var('h')
A = t.placeholder((1024, 1024))
B = t.placeholder((1024, 1024))
k = t.reduce_axis((0, 1024))
C = t.compute((1024, 1024), lambda y, x: t.sum(A[k, y] * B[k, x], axis=k))
2.5 Schedule
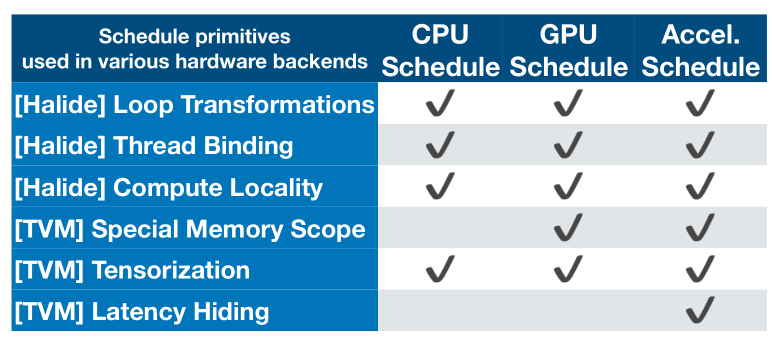
TVM的Schedule参考Halide, 主要包含以下方式:
- Split
- Tile
- Reorder
- Bind
- …
其与Halide的异同如下图:
2.6 TOPI
TOPI – TVM Operator Inventory, Like numpy.
from __future__ import absolute_import, print_function
import tvm
import topi
import numpy as np
功能:
- Numpy式运算符重载
- Schedule 和 Fusing
- 针对不同的后端具有不同的实现以优化性能。对于每个后端,必须在计算声明和计划的目标范围内调用它们。TVM将选择正确的功能来调用目标信息。
参考[4].
3. TensorFlow XLA
XLA:Accelerated Linear Algebra; 是线性代数的特定于域的编译器,可优化TensorFlow计算。结果是服务器和移动平台的速度,内存使用和可移植性方面的改进.
其结构在框图如下:
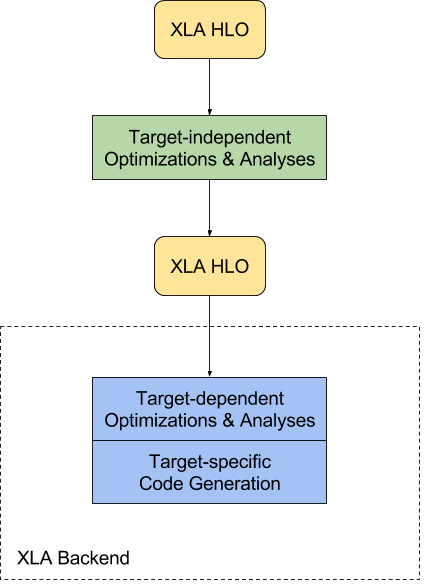
其主要的优化与作用:
-
Improve execution speed. Compile subgraphs to reduce the execution time of short-lived Ops to eliminate overhead from the TensorFlow runtime, fuse pipelined operations to reduce memory overhead, and specialize to known tensor shapes to allow for more aggressive constant propagation.
-
Improve memory usage. Analyze and schedule memory usage, in principle eliminating many intermediate storage buffers.
-
Reduce reliance on custom Ops. Remove the need for many custom Ops by improving the performance of automatically fused low-level Ops to match the performance of custom Ops that were fused by hand.
-
Reduce mobile footprint. Eliminate the TensorFlow runtime by ahead-of-time compiling the subgraph and emitting an object/header file pair that can be linked directly into another application. The results can reduce the footprint for mobile inference by several orders of magnitude.
-
Improve portability. Make it relatively easy to write a new backend for novel hardware, at which point a large fraction of TensorFlow programs will run unmodified on that hardware. This is in contrast with the approach of specializing individual monolithic Ops for new hardware, which requires TensorFlow programs to be rewritten to make use of those Ops.
参考[5].
相关资料:
XLA: TensorFlow Compiled! Video DOC
4. nGraph
nGraph Compiler旨在使用任何深度学习框架加速开发AI工作负载,并部署到各种硬件目标。我们坚信为AI开发人员提供自由,性能和易用性。
官方网站: https://www.intel.ai/ngraph/
官方文档: DOC
其流程图如下:
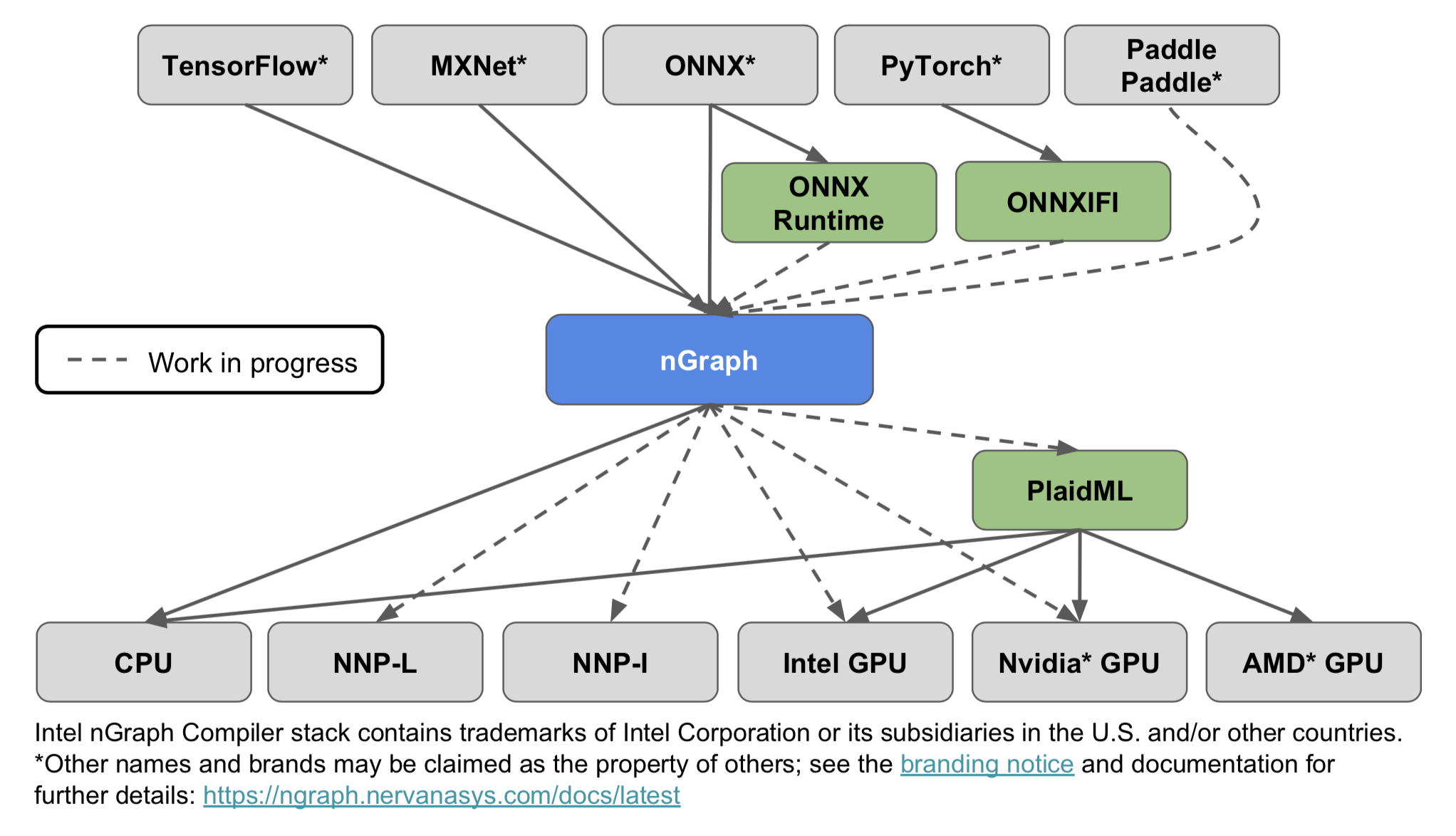
上图显示了nGraph支持的深度学习框架和硬件目标。图中的NNP-L和NNP-I指的是英特尔下一代深度学习加速器:分别用于学习和推理的英特尔Nervana神经网络处理器。生态系统部分概述了支持附加深度学习框架和后端的未来计划
其定义了 nGraph IR.
其前端和后端的支持如下表:
| 前端 | 后端 |
|---|---|
| TensorFlow | Intel CPU |
| MXNet | Intel GPU |
| ONNX | N GPU |
| Pytorch | A GPU |
| Paddle | A CPU |
| Custom Acc |
参考[6].
5. DLVM
DLVM: Deep Learning Virtual Machine.
结构图如下:
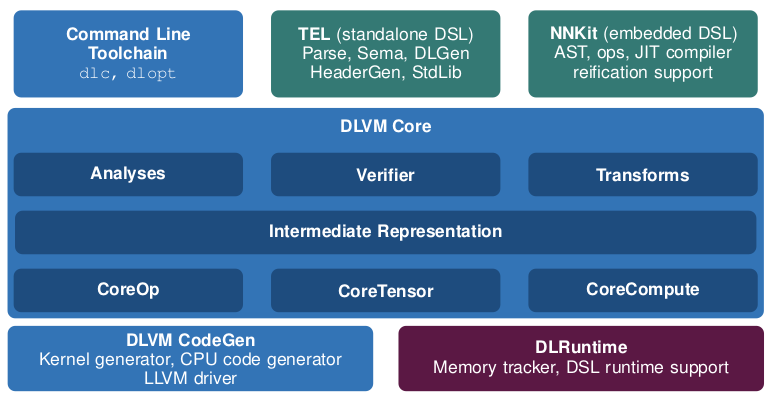
DLVM是一种用于深度学习系统的新编译器基础架构,可解决现有深度学习框架的不足之处。我们的解决方案包括:
(1)专门用于张量计算的领域特定中间表示;
(2)原理使用现代编译器优化技术来大幅简化神经网络计算,包括代数简化,AD检查点,计算核融合和各种传统的编译器优化;
(3)通过成熟的编译器基础设施生成代码,允许透明地定位各种硬件;
(4)支持静态分析,类型安全和张量计算的自然表达的嵌入式DSL,并且具有实时(JIT)编译器,针对DLVM进行AD,优化和代码生成。
前端框架与后端支持:
| Frame Work | Back-end |
|---|---|
| DSL(Domain-Specific Language) | CPU |
| ~TensorFlow | LLVM |
| ~HPVM |
参考[7].
Reference
[1]: TVM Group [OL], 2019.07.14, https://tvm.ai/about
[2]: 陈天奇@如何评价陈天奇团队新开源的TVM [OL], 2019.07.14, https://www.zhihu.com/question/64091792
[3]: CHEN T, MOREAU T, JIANG Z, 等. TVM: An Automated End-to-End Optimizing Compiler for Deep Learning[J]. arXiv:1802.04799 [cs], 2018.
[4]: TOPI, [OL], 2019.07.16, https://docs.tvm.ai/tutorials/topi/intro_topi.html
[5]: XLA Overview, 2019.07.17 https://tensorflow.google.cn/xla/overview
[6]: CYPHERS S, BANSAL A K, BHIWANDIWALLA A, 等. Intel nGraph: An Intermediate Representation, Compiler, and Executor for Deep Learning[J]. arXiv:1801.08058 [cs], 2018.
[7]: WEI R, SCHWARTZ L, ADVE V. DLVM: A modern compiler infrastructure for deep learning systems[J]. arXiv:1711.03016 [cs], 2017.
